Global Warming & Climate Change Difference, Relationship ,Compare & Contrast Article
Global warming and climate change, while often used interchangeably, denote distinct yet closely connected phenomena.
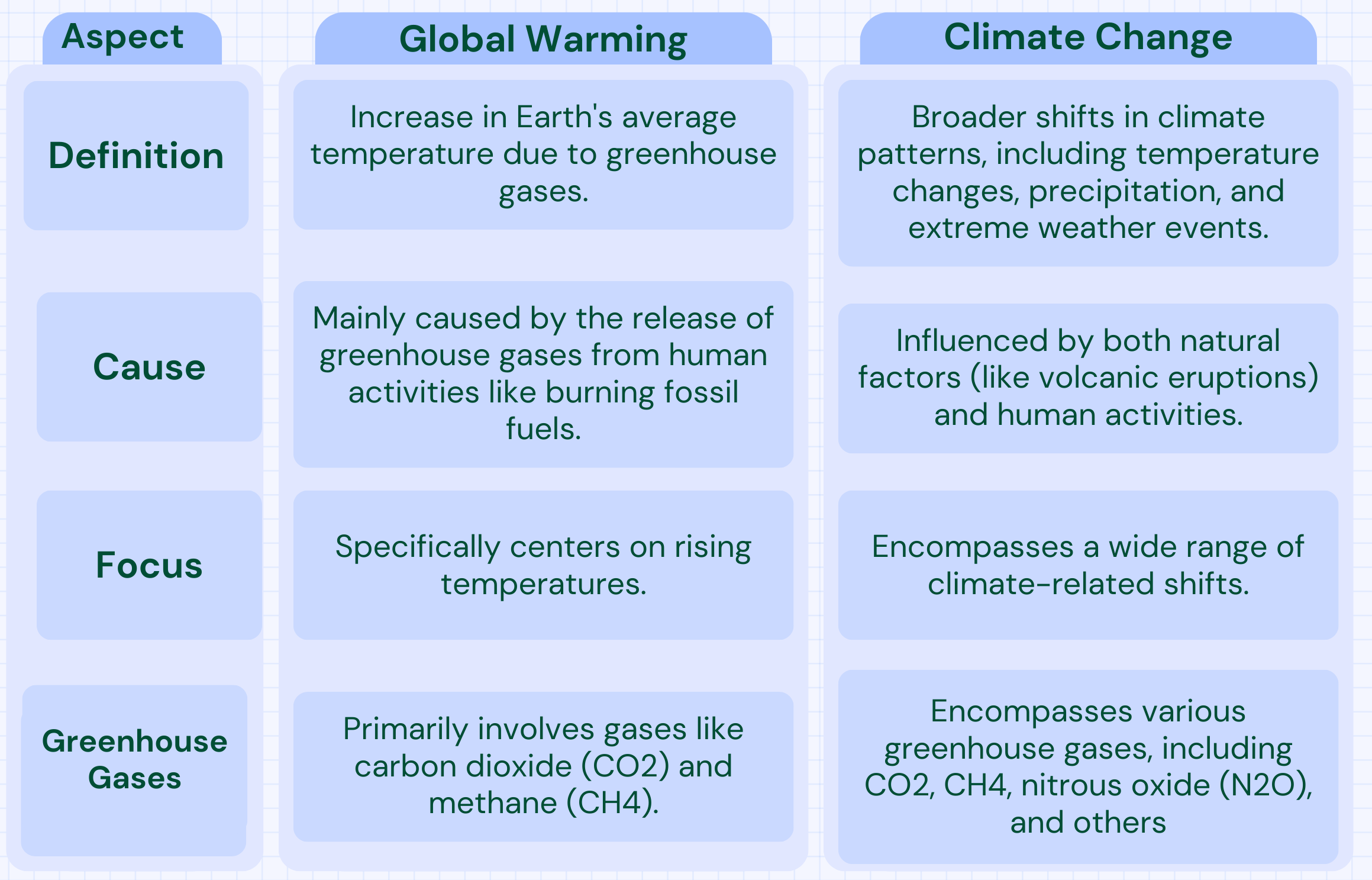
Global warming is the gradual increase in Earth's overall temperature caused by the accumulation of heat-trapping gases in the atmosphere. It is primarily caused by human activities, particularly the release of certain gases into the atmosphere.

These gases are known as greenhouse gases and include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. This trapped heat causes the planet's temperature to rise over time. Earth's average temperature has increased by about 1.2 degrees Celsius (2.2 degrees Fahrenheit) since the late 19th century.
On the other hand, climate change broader term that includes various shifts in Earth's climate patterns. It includes not only rising temperatures but also shifts in rainfall patterns, ocean levels, and the occurrence and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods. Climate change is influenced by both natural factors (such as volcanic eruptions and solar radiation) and human activities. Human activities like deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture also play a significant role in climate change.
Relationship between Global Warming and Climate Change:
Global warming is a crucial component of climate change. It acts as the driving force behind many of the observable changes in our climate. As Earth's temperature rises, it initiates a series of cascading effects on our planet's climate dynamics. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, shifts in weather patterns, and intensified extreme events are all interconnected consequences. Global warming acts as the driving force behind these shifts, illustrating its profound connection to the larger story of climate change. Recognizing this interdependence is crucial in tackling not only the immediate warming trend but also its extensive implications for our environment.

Here are two examples of how global warming triggers climate change:
1. Melting Arctic Ice: The consequences of global warming are vividly apparent in the Arctic region, where ice is rapidly vanishing. As the ice disappears, it reduces the Earth's reflectivity, leading to more sunlight being absorbed by the ocean. This process amplifies warming trends in the Arctic, with far-reaching effects on global weather patterns and potential disruptions to ocean currents.
2. Changing Rainfall Patterns: Additionally, global warming leads to shifts in precipitation patterns, exacerbating droughts in some regions and intensifying rainfall in others. For instance, California faces prolonged droughts, impacting agriculture and water supply, while areas like South Asia experience more intense monsoons, causing flooding and landslides.
These instances serve as compelling examples of how global warming serves as a catalyst for climate change, causing widespread impacts on ecosystems, altering weather dynamics, and profoundly affecting human societies. Comprehending both concepts is vital, as tackling global warming constitutes a pivotal step in alleviating the overarching repercussions of climate change.
